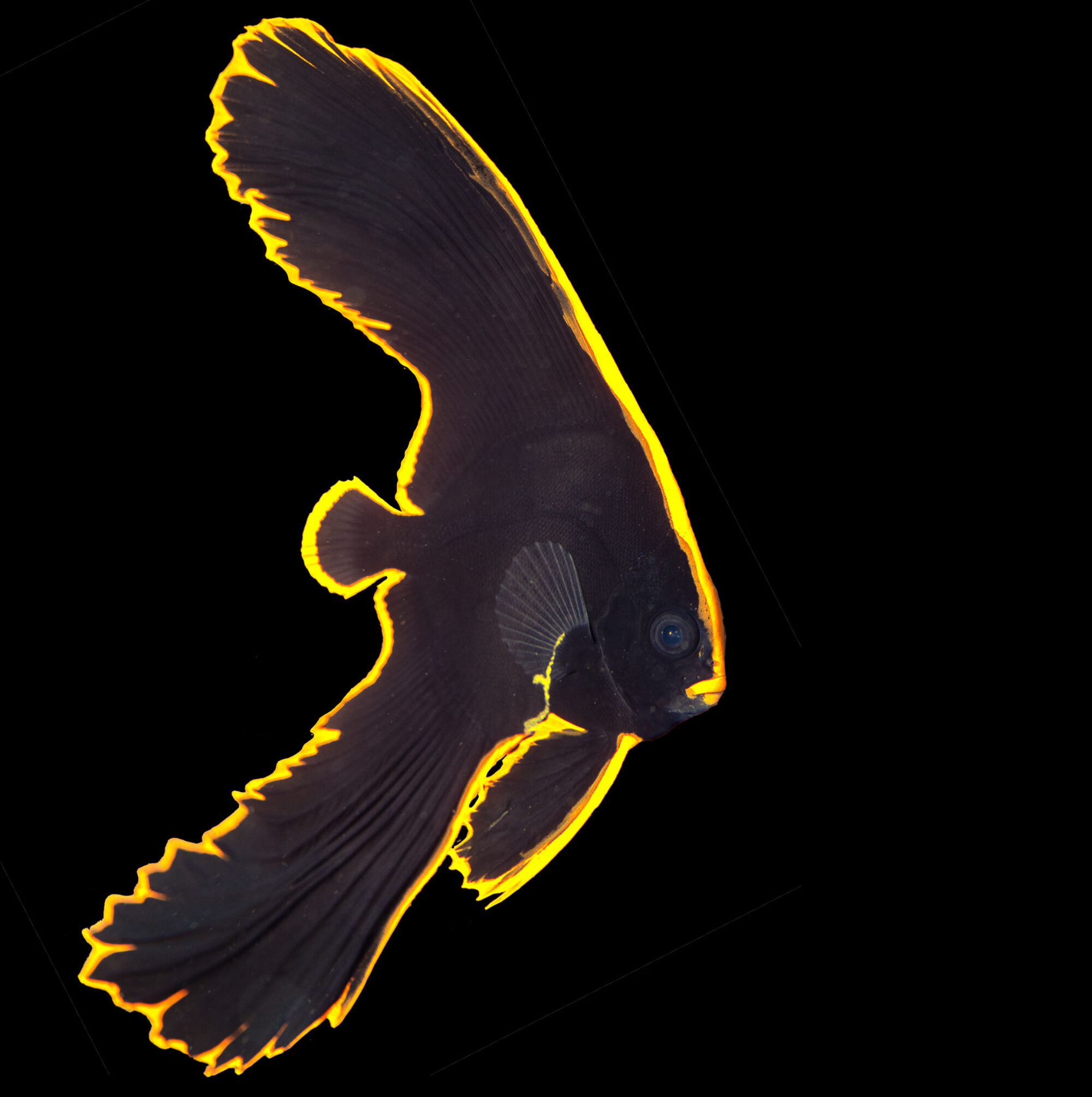
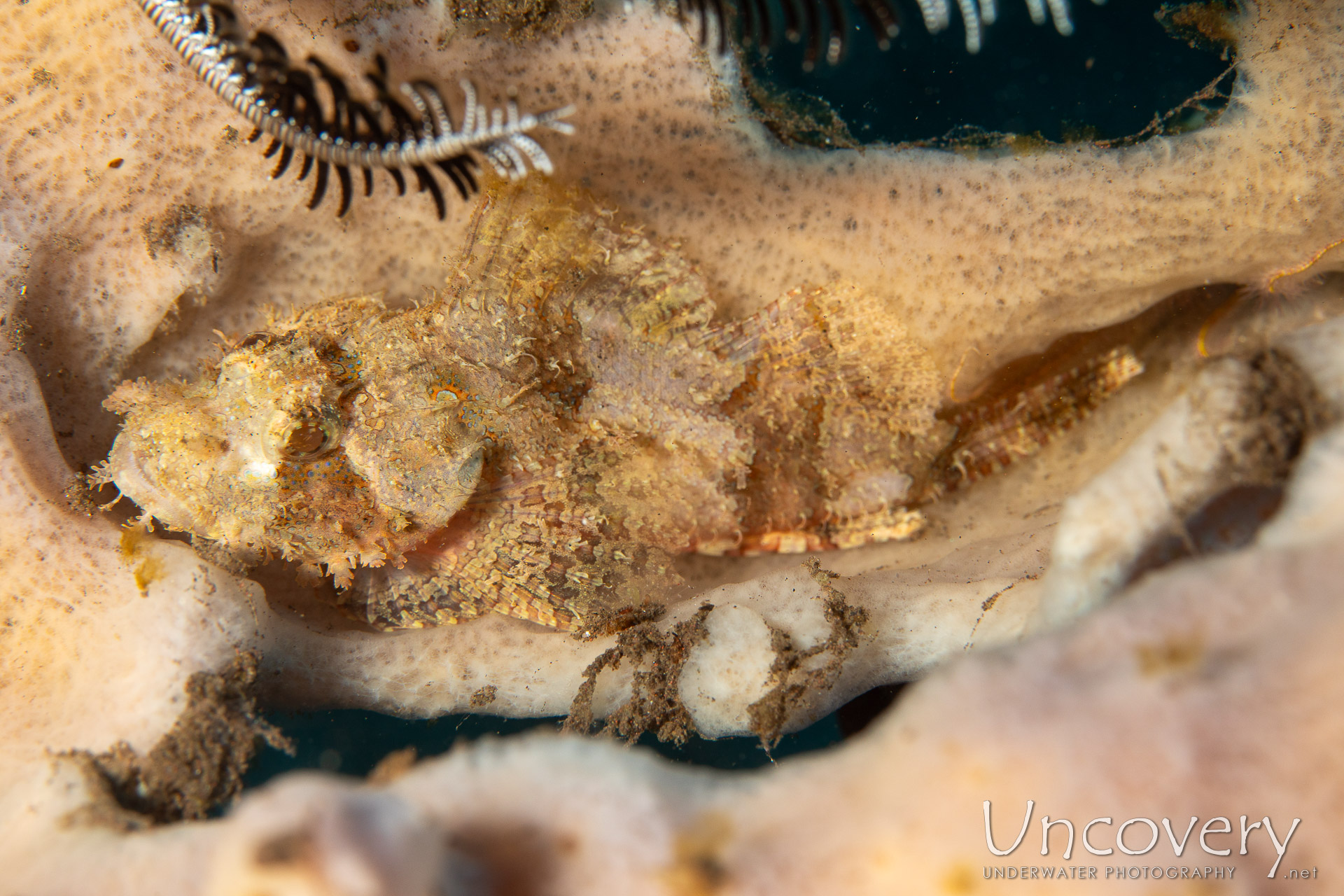
Species images
















































































This species has been seen on the following dives:
- Tulamben, Bali, 26th August ’23: Batu Niti
- Tulamben, Bali, 24th August ’23: Emerald
- Tulamben, Bali, 22nd August ’23: Pantai Lahar
- Tulamben, Bali, 19th August ’23: Bulakan Slope
- Lembeh, Sulawesi, 29th December 2019: Naemundung
- Lembeh, Sulawesi, 24th December 2019: Goby a Crab
- Tulamben, Bali, 9th August 2019: Batu Niti Reef
- Tulamben, Bali, 6th August 2019: Liberty Wreck
- Tulamben, Bali, 5th August 2019: Batu Lumbang
- Tulamben, Bali, 5th August 2019: Pantai Lahar
- Tulamben, Bali, 4th August 2019: Drop Off
- Tulamben, Bali, 5th January 2019: Batu Niti Reef
- Tulamben, Bali, 31st December 2018: Batu Niti Reef
- Tulamben, Bali, 30th December 2018: Drop Off
- Tulamben, Bali, 28th December 2018: Bulakan Slope 1
- Tulamben, Bali, 25th December 2018: River
- South Male Atoll, July 28th, Kuda Giri
- South Male Atoll, July 22nd, Stage
- South Male Atoll, July 20th, Veligadu Beyru
- Anilao, Philippines, December 26th: Dakeda (Night Dive)
- Anilao, Philippines, December 24th: Basura
- Anilao, Philippines, December 23th: Dakeda
- Anilao, Philippines, December 22th: Aqua Bay
- Anilao, Philippines, December 20th: Mato Point
- Anilao, Philippines, December 19th: Kirby’s Rock
- Tulamben, Bali, July 20th: Ulami
- Tulamben, Bali, July 17th: Seraya Secrets (night dive)
- Tulamben, Bali, July 12th: Batu Niti Slope
- Tulamben, Bali, July 11th: Sidem
- Tulamben, Bali, April 14th: Batu Niti Slope


